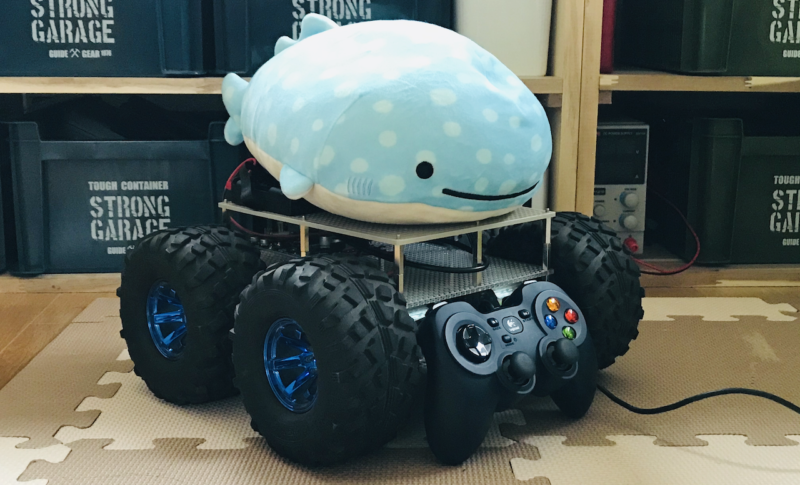

Let’s play with AI.
こんにちは。
AI coordinator管理人の清水秀樹です。
人気のコーナー「外でも動く遠隔操作AIロボットを作ろうpart02:Arduino編」に続き、part03:joystick編です。
part01、part02を見ていない方は以下の動画でご確認頂けます。
今回のpart03も動画で紹介しています。
是非参考にしてみてください。
joystickでタイヤを動かしてみよう。
前回はarduino IDEのシリアルモニタからタイヤを動かしました。
今回はjoystickを使ってタイヤを動かしてみたいと思います。
使用したjoystickはこちらです。
では、早速arduinoに書き込むソースコードの紹介です。
test.ino
<pre class="wp-block-syntaxhighlighter-code">/*
* This example shows how to control MDDS30 in Serial Simplified mode with Arduino.
* Set MDDS30 input mode to 0b11001100
* Open Serial Monitor, set baudrate to 9600bps and "No line ending".
* Send 0: Left motor stops
* 1: Left motor rotates CW with half speed
* 2: Left motor rotates CW with full speed
* 3: Left motor rotates CCW with half speed
* 4: Left motor rotates CCW with full speed
* 5: Right motor stops
* 6: Right motor rotates CW with half speed
* 7: Right motor rotates CW with full speed
* 8: Right motor rotates CCW with half speed
* 9: Right motor rotates CCW with full speed
*
* Note: This example also compatible with MDDS10 and MDDS60
*
* Hardware Connection:
* Arduino Uno MDDS30
* GND ---------- GND
* 4 ------------ IN1
*
* Related Products:
* - SmartDriveDuo-30: http://www.cytron.com.my/P-MDDS60
* - CT UNO: http://www.cytron.com.my/p-ct-uno
* - DC Brush Motors: http://www.cytron.com.my/c-84-dc-motor
* - LiPo Battery: http://www.cytron.com.my/c-87-power/c-97-lipo-rechargeable-battery-and-charger
* - Male to Male Jumper: https://www.cytron.com.my/p-wr-jw-mm65
*
* URL: http://www.cytron.com.my
*/
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
#include <Cytron_SmartDriveDuo.h>
#define IN1 4 // Arduino pin 4 is connected to MDDS60 pin IN1.
#define BAUDRATE 9600
Cytron_SmartDriveDuo smartDriveDuo30(SERIAL_SIMPLFIED, IN1, BAUDRATE);
float motor_L;
float motor_R;
signed int speedLeft, speedRight;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop()
{
if (Serial.available()) {
String motor = Serial.readStringUntil('z');
//Serial.println(motor);
int kg = motor.indexOf(",");
//Serial.println(kg);
int length = motor.length();
//Serial.println(length);
float motor_updown = motor.substring(0, kg).toFloat();
float motor_LR = motor.substring(kg + 1 , length).toFloat();
// Serial.println(motor_updown);
// Serial.println(motor_LR);
if (motor_updown == 0.0 && motor_LR > 0.0) {
motor_L = motor_LR;
motor_R = -motor_LR;
} else if (motor_updown == 0.0 && motor_LR < 0.0) {
motor_L = motor_LR;
motor_R = -motor_LR;
} else if (motor_updown > 0.0 && motor_LR > 0.0) {
motor_L = motor_updown;
motor_R = 0;
} else if (motor_updown < 0.0 && motor_LR > 0.0) {
motor_L = 0;
motor_R = motor_updown;
} else if (motor_updown > 0.0 && motor_LR < 0.0) {
motor_L = 0;
motor_R = motor_updown;
} else if (motor_updown < 0.0 && motor_LR < 0.0) {
motor_L = motor_updown;
motor_R = 0;
} else {
motor_L = motor_updown;
motor_R = motor_updown;
}
speedLeft = motor_L * 100;
speedRight = motor_R * 100;
smartDriveDuo30.control(speedLeft, speedRight);
Serial.flush();
}
}</pre>続いてPC側のjoystickソースコードです。
こちらはpythonを使用します。
joystick_serial_motor.py
<pre class="wp-block-syntaxhighlighter-code">import pygame
from pygame.locals import *
import time
import serial
#シリアル通信(PC⇔Arduino)
ser = serial.Serial()
ser.port = "COM4" #デバイスマネージャでArduinoのポート確認
ser.baudrate = 9600 #Arduinoと合わせる
ser.setDTR(False) #DTRを常にLOWにしReset阻止
ser.open() #COMポートを開く
joy_list = [[0]*3]*3
pygame.joystick.init()
try:
j = pygame.joystick.Joystick(0) # create a joystick instance
j.init() # init instance
print ('Joystickの名称: ' + j.get_name())
print ('ボタン数 : ' + str(j.get_numbuttons()))
#キーが押されたフレーム時間を記録するリストを生成
key_list =[0]*j.get_numbuttons()
except pygame.error:
print ('Joystickが見つかりませんでした。')
def main():
pygame.init()
frametime = 0
x,y =0,0
while 1:
for e in pygame.event.get(): # イベントチェック
if e.type == QUIT: # 終了が押された?
return
if (e.type == KEYDOWN and
e.key == K_ESCAPE): # ESCが押された?
return
# Joystick関連のイベントチェック
#Joystick
if e.type == pygame.locals.JOYAXISMOTION:
joy_list[x][y] = pygame.time.get_ticks() - joy_list[x][y]
print('joystick')
L_stick_LR = '{:.1f}'.format(j.get_axis(0))
L_stick_updown = '{:.1f}'.format(j.get_axis(1))
#符号変換
L_stick_updown = float(L_stick_updown) * -1
L_stick_updown = str(L_stick_updown)
R_stick_LR = '{:.1f}'.format(j.get_axis(4))
R_stick_updown = '{:.1f}'.format(j.get_axis(3))
back_button = '{:.1f}'.format(j.get_axis(2))
print('左スティック:', L_stick_updown, L_stick_LR)
print('右スティック:', R_stick_updown, R_stick_LR)
print('バックスティック:', back_button)
L_stick = L_stick_updown + ',' + L_stick_LR + 'z'
print(L_stick.encode())
ser.write(L_stick.encode())
#十字キー
elif e.type == pygame.locals.JOYHATMOTION:
#print ('hat motion')
x,y = j.get_hat(0)
joy_list[x][y] = pygame.time.get_ticks()
cross_key = str(float(y)) + ',' + str(float(x)) + 'z'
print(cross_key.encode())
ser.write(cross_key.encode())
#各種ボタン押下
elif e.type == pygame.locals.JOYBUTTONDOWN:
print (str(e.button)+'番目のボタンを押した')
key_list[e.button] = pygame.time.get_ticks()
#各種ボタン離脱
elif e.type == pygame.locals.JOYBUTTONUP:
print('ボタン'+str(e.button)+'を離した')
key_list[e.button] = pygame.time.get_ticks() - key_list[e.button]
#print("frame : " + str(key_list[e.button]/1000*60 ))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
ser.close() #COMポートを閉じる
</pre>上記2つのソースコードはgithubでも公開しています。
joystickの十字キーと左スティックを動かしたときにタイヤが回れば成功です。
次回はmqttを使ったpubとsubについて説明します。
それではまた!





LEAVE A REPLY